Vannevar Bush on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Vannevar Bush ( ; March 11, 1890 – June 28, 1974) was an American
 Bush left Tufts in 1919, although he remained employed by AMRAD, and joined the Department of Electrical Engineering at
Bush left Tufts in 1919, although he remained employed by AMRAD, and joined the Department of Electrical Engineering at
 In August 1940, the NDRC began work on a
In August 1940, the NDRC began work on a
 Bush met with Roosevelt and Vice President Henry A. Wallace on October 9, 1941, to discuss the project. He briefed Roosevelt on
Bush met with Roosevelt and Vice President Henry A. Wallace on October 9, 1941, to discuss the project. He briefed Roosevelt on
 After thinking about the potential of augmented memory for several years, Bush set out his thoughts at length in "
After thinking about the potential of augmented memory for several years, Bush set out his thoughts at length in "
 In July 1945, the Kilgore bill was introduced in Congress, proposing the appointment and removal of a single science administrator by the president, with emphasis on applied research, and a patent clause favoring a government monopoly. In contrast, the competing Magnuson bill was similar to Bush's proposal to vest control in a panel of top scientists and civilian administrators with the executive director appointed by them. The Magnuson bill emphasized basic research and protected private patent rights. A compromise Kilgore–Magnuson bill of February 1946 passed the Senate but expired in the House because Bush favored a competing bill that was a virtual duplicate of Magnuson's original bill. A Senate bill was introduced in February 1947 to create the National Science Foundation (NSF) to replace the OSRD. This bill favored most of the features advocated by Bush, including the controversial administration by an autonomous scientific board. The bill passed the Senate and the House, but was pocket vetoed by Truman on August 6, on the grounds that the administrative officers were not properly responsible to either the president or Congress. The OSRD was abolished without a successor organization on December 31, 1947.
Without a
In July 1945, the Kilgore bill was introduced in Congress, proposing the appointment and removal of a single science administrator by the president, with emphasis on applied research, and a patent clause favoring a government monopoly. In contrast, the competing Magnuson bill was similar to Bush's proposal to vest control in a panel of top scientists and civilian administrators with the executive director appointed by them. The Magnuson bill emphasized basic research and protected private patent rights. A compromise Kilgore–Magnuson bill of February 1946 passed the Senate but expired in the House because Bush favored a competing bill that was a virtual duplicate of Magnuson's original bill. A Senate bill was introduced in February 1947 to create the National Science Foundation (NSF) to replace the OSRD. This bill favored most of the features advocated by Bush, including the controversial administration by an autonomous scientific board. The bill passed the Senate and the House, but was pocket vetoed by Truman on August 6, on the grounds that the administrative officers were not properly responsible to either the president or Congress. The OSRD was abolished without a successor organization on December 31, 1947.
Without a
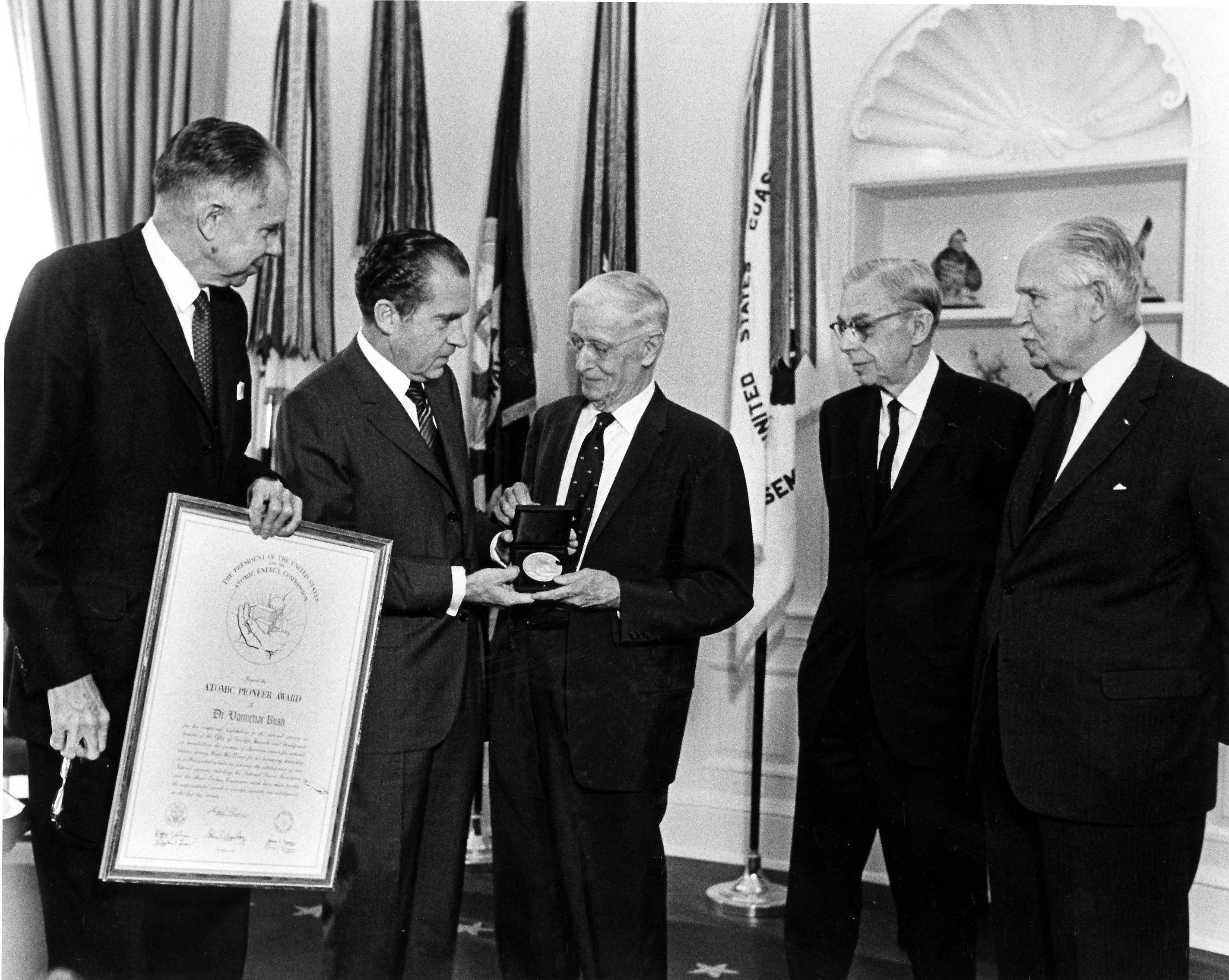 With Truman as president, men like John R. Steelman, who was appointed chairman of the President's Scientific Research Board in October 1946, came to prominence. Bush's authority, both among scientists and politicians, suffered a rapid decline, though he remained a revered figure. In September 1949, he was appointed to head a scientific panel that included Oppenheimer to review the evidence that the Soviet Union had tested its first atomic bomb. The panel concluded that it had, and this finding was relayed to Truman, who made the public announcement. During 1952 Bush was one of five members of the
With Truman as president, men like John R. Steelman, who was appointed chairman of the President's Scientific Research Board in October 1946, came to prominence. Bush's authority, both among scientists and politicians, suffered a rapid decline, though he remained a revered figure. In September 1949, he was appointed to head a scientific panel that included Oppenheimer to review the evidence that the Soviet Union had tested its first atomic bomb. The panel concluded that it had, and this finding was relayed to Truman, who made the public announcement. During 1952 Bush was one of five members of the

Vannevar Bush Papers
MC-0078. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Department of Distinctive Collections, Cambridge, Massachusetts. * * * * * * , - , - , - {{DEFAULTSORT:Bush, Vannevar 1890 births 1974 deaths 20th-century American engineers 20th-century American inventors American electrical engineers American futurologists American people of English descent Burials in Massachusetts Fellows of the American Physical Society Honorary Knights Commander of the Order of the British Empire IEEE Edison Medal recipients IEEE Lamme Medal recipients Internet pioneers Manhattan Project people Medal for Merit recipients MIT School of Engineering alumni MIT School of Engineering faculty National Medal of Science laureates Office of Science and Technology Policy officials People from Chelsea, Massachusetts People from Everett, Massachusetts Raytheon Company people Recipients of the Legion of Honour Tufts University School of Engineering alumni
engineer
Engineers, as practitioners of engineering, are professionals who invent, design, analyze, build and test machines, complex systems, structures, gadgets and materials to fulfill functional objectives and requirements while considering the l ...
, inventor and science administrator, who during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
headed the U.S. Office of Scientific Research and Development
The Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD) was an agency of the United States federal government created to coordinate scientific research for military purposes during World War II. Arrangements were made for its creation during May 1 ...
(OSRD), through which almost all wartime military R&D was carried out, including important developments in radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, w ...
and the initiation and early administration of the Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development undertaking during World War II that produced the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States with the support of the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project w ...
. He emphasized the importance of scientific research to national security and economic well-being, and was chiefly responsible for the movement that led to the creation of the National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent agency of the United States government that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National I ...
.
Bush joined the Department of Electrical Engineering at Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of the ...
(MIT) in 1919, and founded the company that became the Raytheon Company
The Raytheon Company was a major U.S. defense contractor and industrial corporation with manufacturing concentrations in weapons and military and commercial electronics. It was previously involved in corporate and special-mission aircraft unti ...
in 1922. Bush became vice president of MIT and dean of the MIT School of Engineering
The MIT School of Engineering (SoE) is one of the five schools of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, located in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. SoE has eight academic departments and two interdisciplinary institutes. The School gra ...
in 1932, and president of the Carnegie Institution of Washington
The Carnegie Institution of Washington (the organization's legal name), known also for public purposes as the Carnegie Institution for Science (CIS), is an organization in the United States established to fund and perform scientific research. Th ...
in 1938.
During his career, Bush patented a string of his own inventions. He is known particularly for his engineering work on analog computer
An analog computer or analogue computer is a type of computer that uses the continuous variation aspect of physical phenomena such as electrical, mechanical, or hydraulic quantities (''analog signals'') to model the problem being solved. In ...
s, and for the memex
Memex is a hypothetical electromechanical device for interacting with microform documents and described in Vannevar Bush's 1945 article "As We May Think". Bush envisioned the memex as a device in which individuals would compress and store all of ...
.
Starting in 1927, Bush constructed a differential analyzer
The differential analyser is a mechanical analogue computer designed to solve differential equations by integration, using wheel-and-disc mechanisms to perform the integration. It was one of the first advanced computing devices to be used operat ...
, an analog computer with some digital components that could solve differential equation
In mathematics, a differential equation is an equation that relates one or more unknown functions and their derivatives. In applications, the functions generally represent physical quantities, the derivatives represent their rates of change, an ...
s with as many as 18 independent variables. An offshoot of the work at MIT by Bush and others was the beginning of digital circuit In theoretical computer science, a circuit is a model of computation in which input values proceed through a sequence of gates, each of which computes a function. Circuits of this kind provide a generalization of Boolean circuits and a mathematical ...
design theory.
The memex, which he began developing in the 1930s (heavily influenced by Emanuel Goldberg
Emanuel Goldberg ( he, עמנואל גולדברג; yi, עמנואל גאָלדבערג; russian: Эмануэль Гольдберг) (born: 31 August 1881; died: 13 September 1970) was an Israeli physicist and inventor. He was born in Moscow a ...
's "Statistical Machine" from 1928) was a hypothetical adjustable microfilm
Microforms are scaled-down reproductions of documents, typically either photographic film, films or paper, made for the purposes of transmission, storage, reading, and printing. Microform images are commonly reduced to about 4% or of the origin ...
viewer with a structure analogous to that of hypertext
Hypertext is E-text, text displayed on a computer display or other electronic devices with references (hyperlinks) to other text that the reader can immediately access. Hypertext documents are interconnected by hyperlinks, which are typi ...
. The memex and Bush's 1945 essay "As We May Think
"As We May Think" is a 1945 essay by Vannevar Bush which has been described as visionary and influential, anticipating many aspects of information society. It was first published in ''The Atlantic'' in July 1945 and republished in an abridged v ...
" influenced generations of computer scientists, who drew inspiration from his vision of the future.
Bush was appointed to the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics
The National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) was a United States federal agency founded on March 3, 1915, to undertake, promote, and institutionalize aeronautical research. On October 1, 1958, the agency was dissolved and its assets ...
(NACA) in 1938, and soon became its chairman. As chairman of the National Defense Research Committee
The National Defense Research Committee (NDRC) was an organization created "to coordinate, supervise, and conduct scientific research on the problems underlying the development, production, and use of mechanisms and devices of warfare" in the Un ...
(NDRC), and later director of OSRD, Bush coordinated the activities of some six thousand leading American scientists in the application of science to warfare. Bush was a well-known policymaker and public intellectual during World War II, when he was in effect the first presidential science advisor. As head of NDRC and OSRD, he initiated the Manhattan Project, and ensured that it received top priority from the highest levels of government. In ''Science, The Endless Frontier'', his 1945 report to the President of the United States, Bush called for an expansion of government support for science, and he pressed for the creation of the National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent agency of the United States government that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National I ...
.
Early life and education
Vannevar Bush was born inEverett, Massachusetts
Everett is a city in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States, directly north of Boston, bordering the neighborhood of Charlestown. The population was 49,075 at the time of the 2020 United States Census.
Everett was the last city in the Un ...
, on March 11, 1890, the third child and only son of Perry Bush, the local Universalist pastor
A pastor (abbreviated as "Pr" or "Ptr" , or "Ps" ) is the leader of a Christian congregation who also gives advice and counsel to people from the community or congregation. In Lutheranism, Catholicism, Eastern Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodoxy and ...
, and his wife Emma Linwood (née Paine). He had two older sisters, Edith
Edith is a feminine given name derived from the Old English words ēad, meaning 'riches or blessed', and is in common usage in this form in English, German, many Scandinavian languages and Dutch. Its French form is Édith. Contractions and var ...
and Reba. He was named after John Vannevar, an old friend of the family who had attended Tufts College
Tufts University is a private research university on the border of Medford and Somerville, Massachusetts. It was founded in 1852 as Tufts College by Christian universalists who sought to provide a nonsectarian institution of higher learning. ...
with Perry. The family moved to Chelsea, Massachusetts
Chelsea is a city in Suffolk County, Massachusetts, Suffolk County, Massachusetts, United States, directly across the Mystic River from the city of Boston. As of the 2020 census, Chelsea had a population of 40,787. With a total area of just 2.46 s ...
, in 1892, and Bush graduated from Chelsea High School in 1909.
He then attended Tufts College
Tufts University is a private research university on the border of Medford and Somerville, Massachusetts. It was founded in 1852 as Tufts College by Christian universalists who sought to provide a nonsectarian institution of higher learning. ...
, like his father before him. A popular student, he was vice president of his sophomore
In the United States, a sophomore ( or ) is a person in the second year at an educational institution; usually at a secondary school or at the college and university level, but also in other forms of post-secondary educational institutions. In ...
class, and president of his junior
Junior or Juniors may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Music
* ''Junior'' (Junior Mance album), 1959
* ''Junior'' (Röyksopp album), 2009
* ''Junior'' (Kaki King album), 2010
* ''Junior'' (LaFontaines album), 2019
Films
* ''Junior'' (1994 ...
class. During his senior
Senior (shortened as Sr.) means "the elder" in Latin and is often used as a suffix for the elder of two or more people in the same family with the same given name, usually a parent or grandparent. It may also refer to:
* Senior (name), a surname ...
year, he managed the football team. He became a member of the Alpha Tau Omega
Alpha Tau Omega (), commonly known as ATO, is an American social fraternity founded at the Virginia Military Institute in 1865 by Otis Allan Glazebrook. The fraternity has around 250 active and inactive chapters and colonies in the United Stat ...
fraternity, and dated Phoebe Clara Davis, who also came from Chelsea. Tufts allowed students to gain a master's degree
A master's degree (from Latin ) is an academic degree awarded by universities or colleges upon completion of a course of study demonstrating mastery or a high-order overview of a specific field of study or area of professional practice.
in four years simultaneously with a bachelor's degree
A bachelor's degree (from Middle Latin ''baccalaureus'') or baccalaureate (from Modern Latin ''baccalaureatus'') is an undergraduate academic degree awarded by colleges and universities upon completion of a course of study lasting three to six ...
. For his master's thesis
A thesis ( : theses), or dissertation (abbreviated diss.), is a document submitted in support of candidature for an academic degree or professional qualification presenting the author's research and findings.International Standard ISO 7144: ...
, Bush invented and patented a "profile tracer". This was a mapping device for assisting surveyors that looked like a lawn mower. It had two bicycle wheels, and a pen that plotted the terrain over which it traveled. It was the first of a string of inventions. On graduation in 1913 he received both Bachelor of Science
A Bachelor of Science (BS, BSc, SB, or ScB; from the Latin ') is a bachelor's degree awarded for programs that generally last three to five years.
The first university to admit a student to the degree of Bachelor of Science was the University of ...
and Master of Science
A Master of Science ( la, Magisterii Scientiae; abbreviated MS, M.S., MSc, M.Sc., SM, S.M., ScM or Sc.M.) is a master's degree in the field of science awarded by universities in many countries or a person holding such a degree. In contrast to ...
degrees.
After graduation, Bush worked at General Electric
General Electric Company (GE) is an American multinational conglomerate founded in 1892, and incorporated in New York state and headquartered in Boston. The company operated in sectors including healthcare, aviation, power, renewable energ ...
(GE) in Schenectady, New York
Schenectady () is a city in Schenectady County, New York, United States, of which it is the county seat. As of the 2020 census, the city's population of 67,047 made it the state's ninth-largest city by population. The city is in eastern New Y ...
, for $14 a week. As a "test man", his job was to assess equipment to ensure that it was safe. He transferred to GE's plant in Pittsfield, Massachusetts
Pittsfield is the largest city and the county seat of Berkshire County, Massachusetts, United States. It is the principal city of the Pittsfield, Massachusetts Metropolitan Statistical Area which encompasses all of Berkshire County. Pittsfield� ...
, to work on high voltage transformer
A transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer' ...
s, but after a fire broke out at the plant, Bush and the other test men were suspended. He returned to Tufts in October 1914 to teach mathematics, and spent the 1915 summer break working at the Brooklyn Navy Yard
The Brooklyn Navy Yard (originally known as the New York Navy Yard) is a shipyard and industrial complex located in northwest Brooklyn in New York City, New York. The Navy Yard is located on the East River in Wallabout Bay, a semicircular bend ...
as an electrical inspector.
Bush was awarded a $1,500 scholarship to study at Clark University
Clark University is a private research university in Worcester, Massachusetts. Founded in 1887 with a large endowment from its namesake Jonas Gilman Clark, a prominent businessman, Clark was one of the first modern research universities in the ...
as a doctoral student of Arthur Gordon Webster
Arthur Gordon Webster (November 28, 1863 – May 15, 1923) was an American physicist who founded the American Physical Society.
Biography
Webster was born on November 28, 1863, at Brookline, Massachusetts, to William Edward Webster and Mary Sha ...
, but Webster wanted Bush to study acoustics, a popular field at the time that led many to computer science
Computer science is the study of computation, automation, and information. Computer science spans theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, information theory, and automation) to Applied science, practical discipli ...
. Bush preferred to quit rather than study a subject that did not interest him.
Bush subsequently enrolled in the Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of the ...
(MIT) electrical engineering program. Spurred by the need for enough financial security to marry, he submitted his thesis, entitled ''Oscillating-Current Circuits: An Extension of the Theory of Generalized Angular Velocities, with Applications to the Coupled Circuit and the Artificial Transmission Line'', in April 1916. His adviser, Arthur Edwin Kennelly
Arthur Edwin Kennelly (December 17, 1861 – June 18, 1939) was an American electrical engineer.
Biography
Kennelly was born December 17, 1861, in Colaba, in Bombay Presidency, British India, and was educated at University College School in Lond ...
, demanded more work from him, but Bush refused, and Kennelly was overruled by the department chairman. Bush received his doctorate in engineering jointly from MIT and Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
. He married Phoebe in August 1916. They had two sons: Richard Davis Bush and John Hathaway Bush.
Early engineering activities
Bush accepted a job with Tufts, where he became involved with the American Radio and Research Corporation (AMRAD), which began broadcasting music from the campus on March 8, 1916. The station owner, Harold Power, hired him to run the company's laboratory, at a salary greater than that which Bush drew from Tufts. In 1917, following the United States' entry into World War I, he went to work with theNational Research Council National Research Council may refer to:
* National Research Council (Canada), sponsoring research and development
* National Research Council (Italy), scientific and technological research, Rome
* National Research Council (United States), part of ...
. He attempted to develop a means of detecting submarines by measuring the disturbance in the Earth's magnetic field. His device worked as designed, but only from a wooden ship; attempts to get it to work on a metal ship such as a destroyer
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort
larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against powerful short range attackers. They were originally developed in ...
failed.
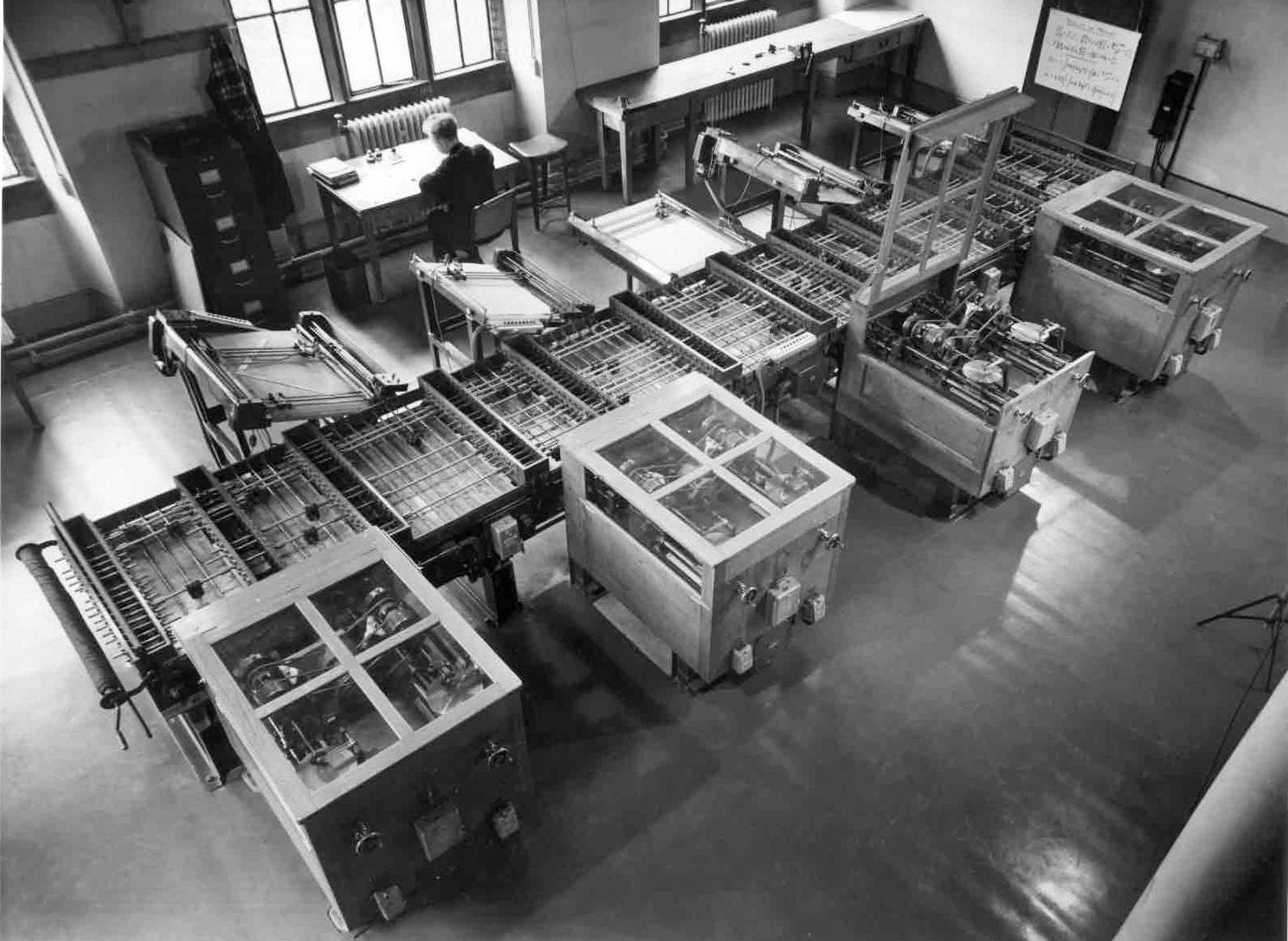
 Bush left Tufts in 1919, although he remained employed by AMRAD, and joined the Department of Electrical Engineering at
Bush left Tufts in 1919, although he remained employed by AMRAD, and joined the Department of Electrical Engineering at Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of the ...
(MIT), where he worked under Dugald C. Jackson
Dugald Caleb Jackson (13 February, 1865, Kennett Square – July 1, 1951) was an American electrical engineer. He received the IEEE Edison Medal for "outstanding and inspiring leadership in engineering education and in the field of generation an ...
. In 1922, he collaborated with fellow MIT professor William H. Timbie on ''Principles of Electrical Engineering'', an introductory textbook. AMRAD's lucrative contracts from World War I had been cancelled, and Bush attempted to reverse the company's fortunes by developing a thermostatic switch invented by Al Spencer, an AMRAD technician, on his own time. AMRAD's management was not interested in the device, but had no objection to its sale. Bush found backing from Laurence K. Marshall and Richard S. Aldrich
Richard Steere Aldrich (February 29, 1884December 25, 1941) was an American politician. He was a Republican member of the U.S. House of Representatives, and served in the Rhode Island State Senate and the Rhode Island House of Representatives. ...
to create the Spencer Thermostat Company, which hired Bush as a consultant. The new company soon had revenues in excess of a million dollars. It merged with General Plate Company to form Metals & Controls Corporation in 1931, and with Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is an American technology company headquartered in Dallas, Texas, that designs and manufactures semiconductors and various integrated circuits, which it sells to electronics designers and manufacturers globall ...
in 1959. Texas Instruments sold it to Bain Capital
Bain Capital is an American private investment firm based in Boston. It specializes in private equity, venture capital, credit, public equity, impact investing, life sciences, and real estate. Bain Capital invests across a range of industry se ...
in 2006, and it became a separate company again as Sensata Technologies in 2010.
In 1924, Bush and Marshall teamed up with physicist Charles G. Smith, who had invented a voltage-regulator tube
A voltage-regulator tube (VR tube) is an electronic component used as a shunt regulator to hold a voltage constant at a pre-determined level.
Physically, these devices resemble vacuum tubes, but there are two main differences:
* Their glass env ...
called the S-tube. The device enabled radios, which had previously required two different types of batteries, to operate from mains power
Mains electricity or utility power, power grid, domestic power, and wall power, or in some parts of Canada as hydro, is a general-purpose alternating-current (AC) electric power supply. It is the form of electrical power that is delivered to ...
. Marshall had raised $25,000 to set up the American Appliance Company on July 7, 1922, to build silent refrigerators, with Bush and Smith among its five directors, but changed course and renamed it the Raytheon Company
The Raytheon Company was a major U.S. defense contractor and industrial corporation with manufacturing concentrations in weapons and military and commercial electronics. It was previously involved in corporate and special-mission aircraft unti ...
, to make and market the S-tube. The venture made Bush wealthy, and Raytheon ultimately became a large electronics company and defense contractor
The arms industry, also known as the arms trade, is a global industry which manufactures and sells weapons and military technology. It consists of a commercial industry involved in the research and development, engineering, production, and serv ...
.
Starting in 1927, Bush constructed a differential analyzer
The differential analyser is a mechanical analogue computer designed to solve differential equations by integration, using wheel-and-disc mechanisms to perform the integration. It was one of the first advanced computing devices to be used operat ...
, an analog computer
An analog computer or analogue computer is a type of computer that uses the continuous variation aspect of physical phenomena such as electrical, mechanical, or hydraulic quantities (''analog signals'') to model the problem being solved. In ...
that could solve differential equation
In mathematics, a differential equation is an equation that relates one or more unknown functions and their derivatives. In applications, the functions generally represent physical quantities, the derivatives represent their rates of change, an ...
s with as many as 18 independent variables. This invention arose from previous work performed by Herbert R. Stewart, one of Bush's master's students, who at Bush's suggestion created the integraph, a device for solving first-order differential equation
In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation (ODE) is a differential equation whose unknown(s) consists of one (or more) function(s) of one variable and involves the derivatives of those functions. The term ''ordinary'' is used in contrast ...
s, in 1925. Another student, Harold Hazen, proposed extending the device to handle second-order differential equation
In mathematics, a differential equation is an equation that relates one or more unknown functions and their derivatives. In applications, the functions generally represent physical quantities, the derivatives represent their rates of change, and ...
s. Bush immediately realized the potential of such an invention, for these were much more difficult to solve, but also quite common in physics. Under Bush's supervision, Hazen was able to construct the differential analyzer, a table-like array of shafts and pens that mechanically simulated and plotted the desired equation. Unlike earlier designs that were purely mechanical, the differential analyzer had both electrical and mechanical components. Among the engineers who made use of the differential analyzer was General Electric
General Electric Company (GE) is an American multinational conglomerate founded in 1892, and incorporated in New York state and headquartered in Boston. The company operated in sectors including healthcare, aviation, power, renewable energ ...
's Edith Clarke
Edith Clarke (February 10, 1883 – October 29, 1959) was the first woman to be professionally employed as an electrical engineer in the United States, and the first female professor of electrical engineering in the country. She was the first ...
, who used it to solve problems relating to electric power transmission. For developing the differential analyzer, Bush was awarded the Franklin Institute
The Franklin Institute is a science museum and the center of science education and research in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It is named after the American scientist and statesman Benjamin Franklin. It houses the Benjamin Franklin National Memori ...
's Louis E. Levy Medal
The Franklin Institute is a science museum and the center of science education and research in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It is named after the American scientist and wikt:statesman, statesman Benjamin Franklin. It houses the Benjamin Franklin ...
in 1928.
Bush taught boolean algebra
In mathematics and mathematical logic, Boolean algebra is a branch of algebra. It differs from elementary algebra in two ways. First, the values of the variables are the truth values ''true'' and ''false'', usually denoted 1 and 0, whereas in e ...
, circuit theory
Circuit may refer to:
Science and technology
Electrical engineering
* Electrical circuit, a complete electrical network with a closed-loop giving a return path for current
** Analog circuit, uses continuous signal levels
** Balanced circui ...
, and operational calculus Operational calculus, also known as operational analysis, is a technique by which problems in analysis, in particular differential equations, are transformed into algebraic problems, usually the problem of solving a polynomial equation.
History
Th ...
according to the methods of Oliver Heaviside
Oliver Heaviside FRS (; 18 May 1850 – 3 February 1925) was an English self-taught mathematician and physicist who invented a new technique for solving differential equations (equivalent to the Laplace transform), independently developed vec ...
while Samuel Wesley Stratton
Samuel Wesley Stratton (July 18, 1861 – October 18, 1931) was an administrator in the American government, physicist, and educator.
Life and work
Stratton was born on farm in Litchfield, Illinois on July 18, 1861. In his youth he kept farm ma ...
was President of MIT. When Harold Jeffreys
Sir Harold Jeffreys, FRS (22 April 1891 – 18 March 1989) was a British mathematician, statistician, geophysicist, and astronomer. His book, ''Theory of Probability'', which was first published in 1939, played an important role in the revival ...
in Cambridge, England, offered his mathematical treatment in ''Operational Methods in Mathematical Physics'' (1927), Bush responded with his seminal textbook ''Operational Circuit Analysis'' (1929) for instructing electrical engineering students. In the preface he wrote:
Parry Moon
Parry Hiram Moon (; February 14, 1898 – March 4, 1988) was an American electrical engineer who, with Domina Eberle Spencer, co-wrote eight scientific books and over 200 papers on subjects including electromagnetic field theory, color harmony, n ...
and Stratton were acknowledged, as was M.S. Vallarta who "wrote the first set of class notes which I used."
An offshoot of the work at MIT was the beginning of digital circuit In theoretical computer science, a circuit is a model of computation in which input values proceed through a sequence of gates, each of which computes a function. Circuits of this kind provide a generalization of Boolean circuits and a mathematical ...
design theory by one of Bush's graduate students, Claude Shannon
Claude Elwood Shannon (April 30, 1916 – February 24, 2001) was an American people, American mathematician, electrical engineering, electrical engineer, and cryptography, cryptographer known as a "father of information theory".
As a 21-year-o ...
. Working on the analytical engine, Shannon described the application of Boolean algebra
In mathematics and mathematical logic, Boolean algebra is a branch of algebra. It differs from elementary algebra in two ways. First, the values of the variables are the truth values ''true'' and ''false'', usually denoted 1 and 0, whereas in e ...
to electronic circuits in his landmark master's thesis, ''A Symbolic Analysis of Relay and Switching Circuits
"A Symbolic Analysis of Relay and Switching Circuits" is the title of a master's thesis written by computer science pioneer Claude E. Shannon while attending the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in 1937. In his thesis, Shannon, a dual ...
''. In 1935, Bush was approached by OP-20-G
OP-20-G or "Office of Chief Of Naval Operations (OPNAV), 20th Division of the Office of Naval Communications, G Section / Communications Security", was the U.S. Navy's signals intelligence and cryptanalysis group during World War II. Its mission ...
, which was searching for an electronic device to aid in codebreaking
Cryptanalysis (from the Greek ''kryptós'', "hidden", and ''analýein'', "to analyze") refers to the process of analyzing information systems in order to understand hidden aspects of the systems. Cryptanalysis is used to breach cryptographic sec ...
. Bush was paid a $10,000 fee to design the Rapid Analytical Machine (RAM). The project went over budget and was not delivered until 1938, when it was found to be unreliable in service. Nonetheless, it was an important step toward creating such a device.
The reform of MIT's administration began in 1930, with the appointment of Karl T. Compton as president. Bush and Compton soon clashed over the issue of limiting the amount of outside consultancy by professors, a battle Bush quickly lost, but the two men soon built a solid professional relationship. Compton appointed Bush to the newly created post of vice president in 1932. That year Bush also became the dean of the MIT School of Engineering
The MIT School of Engineering (SoE) is one of the five schools of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, located in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. SoE has eight academic departments and two interdisciplinary institutes. The School gra ...
. The two positions came with a salary of $12,000 plus $6,000 for expenses per annum.
The companies Bush helped to found and the technologies he brought to the market made him financially secure, so he was able to pursue academic and scientific studies that he felt made the world better in the years before and after World War II.
World War II
Carnegie Institution for Science
In May 1938, Bush accepted a prestigious appointment as president of theCarnegie Institution of Washington
The Carnegie Institution of Washington (the organization's legal name), known also for public purposes as the Carnegie Institution for Science (CIS), is an organization in the United States established to fund and perform scientific research. Th ...
(CIW), which had been founded in Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
Also known as the Carnegie Institution for Science, it had an endowment of $33 million, and annually spent $1.5 million in research, most of which was carried out at its eight major laboratories. Bush became its president on January 1, 1939, with a salary of $25,000. He was now able to influence research policy in the United States at the highest level, and could informally advise the government on scientific matters. Bush soon discovered that the CIW had serious financial problems, and he had to ask the Carnegie Corporation
The Carnegie Corporation of New York is a philanthropic fund established by Andrew Carnegie in 1911 to support education programs across the United States, and later the world. Carnegie Corporation has endowed or otherwise helped to establis ...
for additional funding.
Bush clashed over leadership of the institute with Cameron Forbes, CIW's chairman of the board, and with his predecessor, John Merriam, who continued to offer unwanted advice. A major embarrassment to them all was Harry H. Laughlin, the head of the Eugenics Record Office
The Eugenics Record Office (ERO), located in Cold Spring Harbor, New York, United States, was a research institute that gathered biological and social information about the American population, serving as a center for eugenics and human heredity ...
, whose activities Merriam had attempted to curtail without success. Bush made it a priority to remove him, regarding him as a scientific fraud, and one of his first acts was to ask for a review of Laughlin's work. In June 1938, Bush asked Laughlin to retire, offering him an annuity, which Laughlin reluctantly accepted. The Eugenics Record Office was renamed the Genetics Record Office, its funding was drastically cut, and it was closed completely in 1944. Senator Robert Reynolds attempted to get Laughlin reinstated, but Bush informed the trustees that an inquiry into Laughlin would "show him to be physically incapable of directing an office, and an investigation of his scientific standing would be equally conclusive."
Bush wanted the institute to concentrate on hard science
Hard science and soft science are colloquial terms used to compare scientific fields on the basis of perceived methodological rigor, exactitude, and objectivity. Roughly speaking, the formal sciences & natural sciences are considered "hard", wher ...
. He gutted Carnegie's archeology program, setting the field back many years in the United States. He saw little value in the humanities
Humanities are academic disciplines that study aspects of human society and culture. In the Renaissance, the term contrasted with divinity and referred to what is now called classics, the main area of secular study in universities at the t ...
and social sciences
Social science is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among individuals within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the field of sociology, the original "science of soci ...
, and slashed funding for ''Isis
Isis (; ''Ēse''; ; Meroitic: ''Wos'' 'a''or ''Wusa''; Phoenician: 𐤀𐤎, romanized: ʾs) was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. Isis was first mentioned in the Old Kingd ...
'', a journal dedicated to the history of science and technology and its cultural influence. Bush later explained that "I have a great reservation about these studies where somebody goes out and interviews a bunch of people and reads a lot of stuff and writes a book and puts it on a shelf and nobody ever reads it."
National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics
On August 23, 1938, Bush was appointed to theNational Advisory Committee for Aeronautics
The National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) was a United States federal agency founded on March 3, 1915, to undertake, promote, and institutionalize aeronautical research. On October 1, 1958, the agency was dissolved and its assets ...
(NACA), the predecessor of NASA. Its chairman Joseph Sweetman Ames
Joseph Sweetman Ames (July 3, 1864 – June 24, 1943) was a physicist, professor at Johns Hopkins University, provost of the university from 1926 to 1929, and university president from 1929 to 1935. He is best remembered as one of the founding ...
became ill, and Bush, as vice chairman, soon had to act in his place. In December 1938, NACA asked for $11 million to establish a new aeronautical research laboratory in Sunnyvale, California
Sunnyvale () is a city located in the Santa Clara Valley in northwest Santa Clara County in the U.S. state of California.
Sunnyvale lies along the historic El Camino Real and Highway 101 and is bordered by portions of San Jose to the nort ...
, to supplement the existing Langley Memorial Aeronautical Laboratory. The California location was chosen for its proximity to some of the largest aviation corporations. This decision was supported by the chief of the United States Army Air Corps
The United States Army Air Corps (USAAC) was the aerial warfare service component of the United States Army between 1926 and 1941. After World War I, as early aviation became an increasingly important part of modern warfare, a philosophical r ...
, Major General
Major general (abbreviated MG, maj. gen. and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. The disappearance of the "sergeant" in the title explains the apparent confusion of a ...
Henry H. Arnold
Henry Harley Arnold (June 25, 1886 – January 15, 1950) was an American general officer holding the ranks of General of the Army and later, General of the Air Force. Arnold was an aviation pioneer, Chief of the Air Corps (1938–1941), ...
, and by the head of the navy's Bureau of Aeronautics
The Bureau of Aeronautics (BuAer) was the U.S. Navy's material-support organization for naval aviation from 1921 to 1959. The bureau had "cognizance" (''i.e.'', responsibility) for the design, procurement, and support of naval aircraft and relate ...
, Rear Admiral
Rear admiral is a senior naval flag officer rank, equivalent to a major general and air vice marshal and above that of a commodore and captain, but below that of a vice admiral. It is regarded as a two star "admiral" rank. It is often regarde ...
Arthur B. Cook, who between them were planning to spend $225 million on new aircraft in the year ahead. However, Congress was not convinced of its value, and Bush had to appear before the Senate Appropriations Committee
The United States Senate Committee on Appropriations is a standing committee of the United States Senate. It has jurisdiction over all discretionary spending legislation in the Senate.
The Senate Appropriations Committee is the largest committ ...
on April 5, 1939. It was a frustrating experience for Bush, since he had never appeared before Congress before, and the senators were not swayed by his arguments. Further lobbying was required before funding for the new center, now known as the Ames Research Center
The Ames Research Center (ARC), also known as NASA Ames, is a major NASA research center at Moffett Federal Airfield in California's Silicon Valley. It was founded in 1939 as the second National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) laborat ...
, was finally approved. By this time, war had broken out in Europe, and the inferiority of American aircraft engines was apparent, in particular the Allison V-1710 which performed poorly at high altitudes and had to be removed from the P-51 Mustang
The North American Aviation P-51 Mustang is an American long-range, single-seat fighter and fighter-bomber used during World War II and the Korean War, among other conflicts. The Mustang was designed in April 1940 by a team headed by James ...
in favor of the British Rolls-Royce Merlin
The Rolls-Royce Merlin is a British liquid-cooled V-12 piston aero engine of 27-litres (1,650 cu in) capacity. Rolls-Royce designed the engine and first ran it in 1933 as a private venture. Initially known as the PV-12, it was later ...
engine. The NACA asked for funding to build a third center in Ohio, which became the Glenn Research Center
NASA John H. Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field is a NASA center within the cities of Brook Park and Cleveland between Cleveland Hopkins International Airport and the Rocky River Reservation of Cleveland Metroparks, with a subsidiary facilit ...
. Following Ames's retirement in October 1939, Bush became chairman of the NACA, with George J. Mead as his deputy. Bush remained a member of the NACA until November 1948.
National Defense Research Committee
During World War I, Bush had become aware of poor cooperation between civilian scientists and the military. Concerned about the lack of coordination in scientific research and the requirements of defense mobilization, Bush proposed the creation of a general directive agency in thefederal government
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-governin ...
, which he discussed with his colleagues. He had the secretary of NACA prepare a draft of the proposed National Defense Research Committee
The National Defense Research Committee (NDRC) was an organization created "to coordinate, supervise, and conduct scientific research on the problems underlying the development, production, and use of mechanisms and devices of warfare" in the Un ...
(NDRC) to be presented to Congress, but after the Germans invaded France in May 1940, Bush decided speed was important and approached President Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
directly. Through the President's uncle, Frederic Delano
Frederic Adrian Delano II (September 10, 1863 – March 28, 1953) was an American railroad president who served as the first Vice Chair of the Federal Reserve from 1914 to 1916. After his term as vice chairman, Delano continued to serve as a membe ...
, Bush managed to set up a meeting with Roosevelt on June 12, 1940, to which he brought a single sheet of paper describing the agency. Roosevelt approved the proposal in 15 minutes, writing "OK – FDR" on the sheet.
With Bush as chairman, the NDRC was functioning even before the agency was officially established by order of the Council of National Defense
The Council of National Defense was a United States organization formed during World War I to coordinate resources and industry in support of the war effort, including the coordination of transportation, industrial and farm production, financial s ...
on June 27, 1940. The organization operated financially on a hand-to-mouth basis with monetary support from the president's emergency fund. Bush appointed four leading scientists to the NDRC: Karl Taylor Compton
Karl Taylor Compton (September 14, 1887 – June 22, 1954) was a prominent American physicist and president of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) from 1930 to 1948.
The early years (1887–1912)
Karl Taylor Compton was born in ...
(president of MIT), James B. Conant
James Bryant Conant (March 26, 1893 – February 11, 1978) was an American chemist, a transformative President of Harvard University, and the first U.S. Ambassador to West Germany. Conant obtained a Ph.D. in Chemistry from Harvard in 1916. ...
(president of Harvard University), Frank B. Jewett
Frank Baldwin Jewett (; September 5, 1879 – November 18, 1949) worked as an engineer for American Telegraph and Telephone where his work demonstrated transatlantic radio telephony using a vacuum-tube transmitter. He was also a physicist and ...
(president of the National Academy of Sciences and chairman of the Board of Directors of Bell Laboratories), and Richard C. Tolman (dean of the graduate school at Caltech); Rear Admiral Harold G. Bowen, Sr. and Brigadier General George V. Strong represented the military. The civilians already knew each other well, which allowed the organization to begin functioning immediately. The NDRC established itself in the administration building at the Carnegie Institution of Washington. Each member of the committee was assigned an area of responsibility, while Bush handled coordination. A small number of projects reported to him directly, such as the S-1 Section
The S-1 Executive Committee laid the groundwork for the Manhattan Project by initiating and coordinating the early research efforts in the United States, and liaising with the Tube Alloys Project in Britain.
In the wake of the discovery of nucle ...
. Compton's deputy, Alfred Loomis, said that "of the men whose death in the Summer of 1940 would have been the greatest calamity for America, the President is first, and Dr. Bush would be second or third."
Bush was fond of saying that "if he made any important contribution to the war effort at all, it would be to get the Army and Navy to tell each other what they were doing." He established a cordial relationship with Secretary of War
The secretary of war was a member of the U.S. president's Cabinet, beginning with George Washington's administration. A similar position, called either "Secretary at War" or "Secretary of War", had been appointed to serve the Congress of the ...
Henry L. Stimson
Henry Lewis Stimson (September 21, 1867 – October 20, 1950) was an American statesman, lawyer, and Republican Party politician. Over his long career, he emerged as a leading figure in U.S. foreign policy by serving in both Republican and D ...
, and Stimson's assistant, Harvey H. Bundy, who found Bush "impatient" and "vain", but said he was "one of the most important, able men I ever knew". Bush's relationship with the navy was more turbulent. Bowen, the director of the Naval Research Laboratory
The United States Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) is the corporate research laboratory for the United States Navy and the United States Marine Corps. It was founded in 1923 and conducts basic scientific research, applied research, technological ...
(NRL), saw the NDRC as a bureaucratic rival, and recommended abolishing it. A series of bureaucratic battles ended with the NRL placed under the Bureau of Ships The United States Navy's Bureau of Ships (BuShips) was established by Congress on 20 June 1940, by a law which consolidated the functions of the Bureau of Construction and Repair (BuC&R) and the Bureau of Engineering (BuEng). The new bureau was to ...
, and Secretary of the Navy
The secretary of the Navy (or SECNAV) is a statutory officer () and the head (chief executive officer) of the Department of the Navy, a military department (component organization) within the United States Department of Defense.
By law, the se ...
Frank Knox
William Franklin Knox (January 1, 1874 – April 28, 1944) was an American politician, newspaper editor and publisher. He was also the Republican vice presidential candidate in 1936, and Secretary of the Navy under Franklin D. Roosevelt during ...
placing an unsatisfactory fitness report in Bowen's personnel file. After the war, Bowen would again try to create a rival to the NDRC inside the navy.
On August 31, 1940, Bush met with Henry Tizard
Sir Henry Thomas Tizard (23 August 1885 – 9 October 1959) was an English chemist, inventor and Rector of Imperial College, who developed the modern "octane rating" used to classify petrol, helped develop radar in World War II, and led the fir ...
, and arranged a series of meetings between the NDRC and the Tizard Mission
The Tizard Mission, officially the British Technical and Scientific Mission, was a British delegation that visited the United States during WWII to obtain the industrial resources to exploit the military potential of the research and development ( ...
, a British scientific delegation. At a meeting On September 19, 1940, the Americans described Loomis and Compton's microwave research. They had an experimental 10 cm wavelength short wave
Shortwave radio is radio transmission using shortwave (SW) radio frequencies. There is no official definition of the band, but the range always includes all of the High frequency, high frequency band (HF), which extends from 3 to 30 MHz (10 ...
radar, but admitted that it did not have enough power and that they were at a dead end. Taffy Bowen and John Cockcroft
Sir John Douglas Cockcroft, (27 May 1897 – 18 September 1967) was a British physicist who shared with Ernest Walton the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1951 for splitting the atomic nucleus, and was instrumental in the development of nuclea ...
of the Tizard Mission then produced a cavity magnetron
The cavity magnetron is a high-power vacuum tube used in early radar systems and currently in microwave ovens and linear particle accelerators. It generates microwaves using the interaction of a stream of electrons with a magnetic field while ...
, a device more advanced than anything the Americans had seen, with a power output of around 10 kW at 10 cm, enough to spot the periscope of a surfaced submarine at night from an aircraft. To exploit the invention, Bush decided to create a special laboratory. The NDRC allocated the new laboratory a budget of $455,000 for its first year. Loomis suggested that the lab should be run by the Carnegie Institution, but Bush convinced him that it would best be run by MIT. The Radiation Laboratory
The Radiation Laboratory, commonly called the Rad Lab, was a microwave and radar research laboratory located at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in Cambridge, Massachusetts. It was first created in October 1940 and operated until 31 ...
, as it came to be known, tested its airborne radar from an Army B-18 on March 27, 1941. By mid-1941, it had developed SCR-584 radar
The SCR-584 (short for '' Set, Complete, Radio # 584'') was an automatic-tracking microwave radar developed by the MIT Radiation Laboratory during World War II. It was one of the most advanced ground-based radars of its era, and became one of th ...
, a mobile radar fire control system for antiaircraft guns.
In September 1940, Norbert Wiener
Norbert Wiener (November 26, 1894 – March 18, 1964) was an American mathematician and philosopher. He was a professor of mathematics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). A child prodigy, Wiener later became an early researcher i ...
approached Bush with a proposal to build a digital computer. Bush declined to provide NDRC funding for it on the grounds that he did not believe that it could be completed before the end of the war. The supporters of digital computers were disappointed at the decision, which they attributed to a preference for outmoded analog technology. In June 1943, the Army provided $500,000 to build the computer, which became ENIAC
ENIAC (; Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) was the first programmable, electronic, general-purpose digital computer, completed in 1945. There were other computers that had these features, but the ENIAC had all of them in one packa ...
, the first general-purpose electronic computer. Having delayed its funding, Bush's prediction proved correct as ENIAC was not completed until December 1945, after the war had ended. His critics saw his attitude as a failure of vision.
Office of Scientific Research and Development
On June 28, 1941, Roosevelt established theOffice of Scientific Research and Development
The Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD) was an agency of the United States federal government created to coordinate scientific research for military purposes during World War II. Arrangements were made for its creation during May 1 ...
(OSRD) with the signing of Executive Order 8807. Bush became director of the OSRD while Conant succeeded him as chairman of the NDRC, which was subsumed into the OSRD. The OSRD was on a firmer financial footing than the NDRC since it received funding from Congress, and had the resources and the authority to develop weapons and technologies with or without the military. Furthermore, the OSRD had a broader mandate than the NDRC, moving into additional areas such as medical research and the mass production of penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' moulds, principally '' P. chrysogenum'' and '' P. rubens''. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum using ...
and sulfa drugs. The organization grew to 850 full-time employees, and produced between 30,000 and 35,000 reports. The OSRD was involved in some 2,500 contracts, worth in excess of $536 million.
Bush's method of management at the OSRD was to direct overall policy, while delegating supervision of divisions to qualified colleagues and letting them do their jobs without interference. He attempted to interpret the mandate of the OSRD as narrowly as possible to avoid overtaxing his office and to prevent duplicating the efforts of other agencies. Bush would often ask: "Will it help to win a war; ''this'' war?" Other challenges involved obtaining adequate funds from the president and Congress and determining apportionment of research among government, academic, and industrial facilities. His most difficult problems, and also greatest successes, were keeping the confidence of the military, which distrusted the ability of civilians to observe security regulations and devise practical solutions, and opposing conscription of young scientists into the armed forces. This became especially difficult as the army's manpower crisis really began to bite in 1944. In all, the OSRD requested deferments for some 9,725 employees of OSRD contractors, of which all but 63 were granted. In his obituary, ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'' described Bush as "a master craftsman at steering around obstacles, whether they were technical or political or bull-headed generals and admirals."
Proximity fuze
 In August 1940, the NDRC began work on a
In August 1940, the NDRC began work on a proximity fuze
A proximity fuze (or fuse) is a Fuze (munitions), fuze that detonates an Explosive material, explosive device automatically when the distance to the target becomes smaller than a predetermined value. Proximity fuzes are designed for targets such ...
, a fuze inside an artillery shell that would explode when it came close to its target. A radar set, along with the batteries to power it, was miniaturized to fit inside a shell, and its glass vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied.
The type kn ...
s designed to withstand the 20,000 g-force
The gravitational force equivalent, or, more commonly, g-force, is a measurement of the type of force per unit mass – typically acceleration – that causes a perception of weight, with a g-force of 1 g (not gram in mass measure ...
of being fired from a gun and 500 rotations per second in flight. Unlike normal radar, the proximity fuze sent out a continuous signal rather than short pulses. The NDRC created a special Section T chaired by Merle Tuve
Merle Anthony Tuve (June 27, 1901 – May 20, 1982) was an American geophysicist who was the Chairman of the Office of Scientific Research and Development's Section T, which was created in August 1940. He was founding director of the Johns Hopkins ...
of the CIW, with Commander
Commander (commonly abbreviated as Cmdr.) is a common naval officer rank. Commander is also used as a rank or title in other formal organizations, including several police forces. In several countries this naval rank is termed frigate captain.
...
William S. Parsons as special assistant to Bush and liaison between the NDRC and the Navy's Bureau of Ordnance The Bureau of Ordnance (BuOrd) was a United States Navy organization, which was responsible for the procurement, storage, and deployment of all naval weapons, between the years 1862 and 1959.
History
Congress established the Bureau in the Departmen ...
(BuOrd). One of CIW staff members that Tuve recruited to Section T in 1940 was James Van Allen
James Alfred Van Allen (September 7, 1914August 9, 2006) was an American space scientist at the University of Iowa. He was instrumental in establishing the field of magnetospheric research in space.
The Van Allen radiation belts were named aft ...
. In April 1942, Bush placed Section T directly under the OSRD, and Parsons in charge. The research effort remained under Tuve but moved to the Johns Hopkins University
Johns Hopkins University (Johns Hopkins, Hopkins, or JHU) is a private university, private research university in Baltimore, Maryland. Founded in 1876, Johns Hopkins is the oldest research university in the United States and in the western hem ...
's Applied Physics Laboratory
The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (Applied Physics Laboratory, or APL) is a not-for-profit University Affiliated Research Center, university-affiliated research center (UARC) in Howard County, Maryland. It is affiliated w ...
(APL), where Parsons was BuOrd's representative. In August 1942, a live firing test was conducted with the newly commissioned cruiser ; three pilotless drone
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft without any human pilot, crew, or passengers on board. UAVs are a component of an unmanned aircraft system (UAS), which includes adding a ground-based controller ...
s were shot down in succession.
To preserve the secret of the proximity fuze, its use was initially permitted only over water, where a dud round could not fall into enemy hands. In late 1943, the Army obtained permission to use the weapon over land. The proximity fuze proved particularly effective against the V-1 flying bomb
The V-1 flying bomb (german: Vergeltungswaffe 1 "Vengeance Weapon 1") was an early cruise missile. Its official Ministry of Aviation (Nazi Germany), Reich Aviation Ministry () designation was Fi 103. It was also known to the Allies as the buz ...
over England, and later Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504,
, in 1944. A version was also developed for use with howitzer
A howitzer () is a long- ranged weapon, falling between a cannon (also known as an artillery gun in the United States), which fires shells at flat trajectories, and a mortar, which fires at high angles of ascent and descent. Howitzers, like ot ...
s against ground targets. Bush met with the Joint Chiefs of Staff
The Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS) is the body of the most senior uniformed leaders within the United States Department of Defense, that advises the president of the United States, the secretary of defense, the Homeland Security Council and the ...
in October 1944 to press for its use, arguing that the Germans would be unable to copy and produce it before the war was over. Eventually, the Joint Chiefs agreed to allow its employment from December 25. In response to the German Ardennes Offensive
The Battle of the Bulge, also known as the Ardennes Offensive, was the last major German offensive campaign on the Western Front during World War II. The battle lasted from 16 December 1944 to 28 January 1945, towards the end of the war in ...
on December 16, 1944, the immediate use of the proximity fuze was authorized, and it went into action with deadly effect. By the end of 1944, proximity fuzes were coming off the production lines at the rate of 40,000 per day. "If one looks at the proximity fuze program as a whole," historian James Phinney Baxter III
James Phinney Baxter III (February 15, 1893 in Portland, Maine – June 17, 1975 in Williamstown, Massachusetts) was an American historian, educator, and academic, who won the 1947 Pulitzer Prize for History for his book ''Scientists Against Time ...
wrote, "the magnitude and complexity of the effort rank it among the three or four most extraordinary scientific achievements of the war."
The German V-1 flying bomb demonstrated a serious omission in OSRD's portfolio: guided missiles. While the OSRD had some success developing unguided rockets, it had nothing comparable to the V-1, the V-2
The V-2 (german: Vergeltungswaffe 2, lit=Retaliation Weapon 2), with the technical name ''Aggregat 4'' (A-4), was the world’s first long-range guided ballistic missile. The missile, powered by a liquid-propellant rocket engine, was develope ...
or the Henschel Hs 293
The Henschel Hs 293 was a World War II German radio-guided glide bomb. It is the first operational anti-shipping missile, first used unsuccessfully on 25 August 1943 and then with increasing success over the next year, ultimately damaging or sink ...
air-to-ship gliding guided bomb. Although the United States trailed the Germans and Japanese in several areas, this represented an entire field that had been left to the enemy. Bush did not seek the advice of Dr. Robert H. Goddard
Robert Hutchings Goddard (October 5, 1882 – August 10, 1945) was an American engineer, professor, physicist, and inventor who is credited with creating and building the world's first Liquid-propellant rocket, liquid-fueled rocket. ...
. Goddard would come to be regarded as America's pioneer of rocketry, but many contemporaries regarded him as a crank. Before the war, Bush had gone on the record as saying, "I don't understand how a serious scientist or engineer can play around with rockets", but in May 1944, he was forced to travel to London to warn General Dwight Eisenhower
Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower (born David Dwight Eisenhower; ; October 14, 1890 – March 28, 1969) was an American military officer and statesman who served as the 34th president of the United States from 1953 to 1961. During World War II, ...
of the danger posed by the V-1 and V-2. Bush could only recommend that the launch sites be bombed, which was done.
Manhattan Project
Bush played a critical role in persuading the United States government to undertake a crash program to create anatomic bomb
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb ...
. When the NDRC was formed, the Committee on Uranium was placed under it, reporting directly to Bush as the Uranium Committee. Bush reorganized the committee, strengthening its scientific component by adding Tuve, George B. Pegram, Jesse W. Beams, Ross Gunn
Ross Gunn (May 12, 1897 – October 15, 1966) was an American physicist who worked on the Manhattan Project during World War II. The New York Times described him as "one of the true fathers of the nuclear submarine program".
From 1927 to 1947, ...
and Harold Urey
Harold Clayton Urey ( ; April 29, 1893 – January 5, 1981) was an American physical chemist whose pioneering work on isotopes earned him the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1934 for the discovery of deuterium. He played a significant role in the d ...
. When the OSRD was formed in June 1941, the Uranium Committee was again placed directly under Bush. For security reasons, its name was changed to the Section S-1.
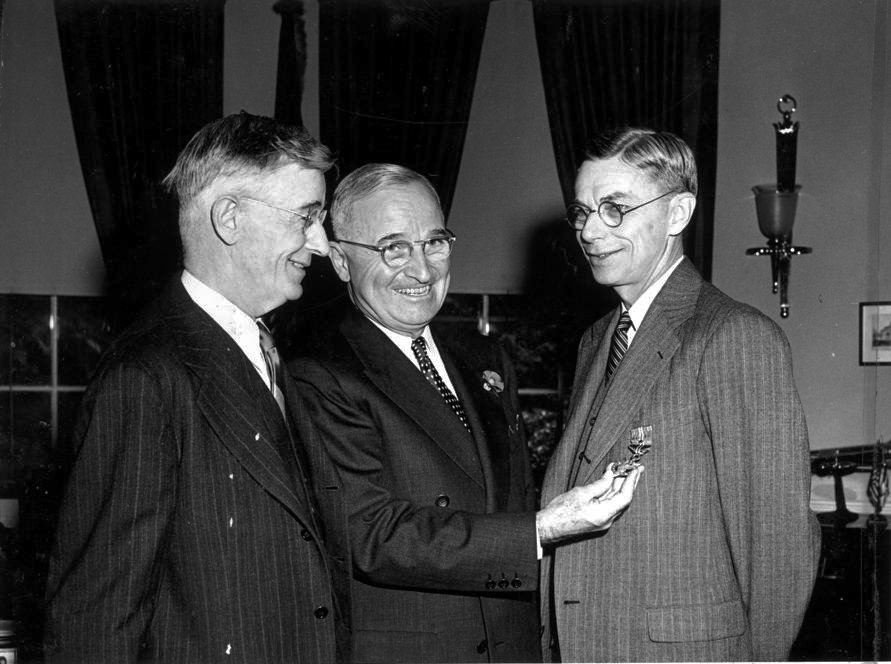
 Bush met with Roosevelt and Vice President Henry A. Wallace on October 9, 1941, to discuss the project. He briefed Roosevelt on
Bush met with Roosevelt and Vice President Henry A. Wallace on October 9, 1941, to discuss the project. He briefed Roosevelt on Tube Alloys
Tube Alloys was the research and development programme authorised by the United Kingdom, with participation from Canada, to develop nuclear weapons during the Second World War. Starting before the Manhattan Project in the United States, the Bri ...
, the British atomic bomb project and its Maud Committee
The MAUD Committee was a British scientific working group formed during the Second World War. It was established to perform the research required to determine if an atomic bomb was feasible. The name MAUD came from a strange line in a telegram fro ...
, which had concluded that an atomic bomb was feasible, and on the German nuclear energy project
The Uranverein ( en, "Uranium Club") or Uranprojekt ( en, "Uranium Project") was the name given to the project in Germany to research nuclear technology, including nuclear weapons and nuclear reactors, during World War II. It went through sev ...
, about which little was known. Roosevelt approved and expedited the atomic program. To control it, he created a Top Policy Group consisting of himself—although he never attended a meeting—Wallace, Bush, Conant, Stimson and the Chief of Staff of the Army, General
A general officer is an Officer (armed forces), officer of highest military ranks, high rank in the army, armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry.
In some usages the term "general officer" refers t ...
George Marshall
George Catlett Marshall Jr. (December 31, 1880 – October 16, 1959) was an American army officer and statesman. He rose through the United States Army to become Chief of Staff of the US Army under Presidents Franklin D. Roosevelt and Harry ...
. On Bush's advice, Roosevelt chose the army to run the project rather than the navy, although the navy had shown far more interest in the field, and was already conducting research into atomic energy for powering ships. Bush's negative experiences with the Navy had convinced him that it would not listen to his advice, and could not handle large-scale construction projects.
In March 1942, Bush sent a report to Roosevelt outlining work by Robert Oppenheimer
J. Robert Oppenheimer (; April 22, 1904 – February 18, 1967) was an American theoretical physicist. A professor of physics at the University of California, Berkeley, Oppenheimer was the wartime head of the Los Alamos Laboratory and is often ...
on the nuclear cross section
The nuclear cross section of a nucleus is used to describe the probability that a nuclear reaction will occur. The concept of a nuclear cross section can be quantified physically in terms of "characteristic area" where a larger area means a larger ...
of uranium-235
Uranium-235 (235U or U-235) is an isotope of uranium making up about 0.72% of natural uranium. Unlike the predominant isotope uranium-238, it is fissile, i.e., it can sustain a nuclear chain reaction. It is the only fissile isotope that exis ...
. Oppenheimer's calculations, which Bush had George Kistiakowsky
George may refer to:
People
* George (given name)
* George (surname)
* George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George
* George Washington, First President of the United States
* George W. Bush, 43rd Preside ...
check, estimated that the critical mass
In nuclear engineering, a critical mass is the smallest amount of fissile material needed for a sustained nuclear chain reaction. The critical mass of a fissionable material depends upon its nuclear properties (specifically, its nuclear fissi ...
of a sphere of Uranium-235
Uranium-235 (235U or U-235) is an isotope of uranium making up about 0.72% of natural uranium. Unlike the predominant isotope uranium-238, it is fissile, i.e., it can sustain a nuclear chain reaction. It is the only fissile isotope that exis ...
was in the range of 2.5 to 5 kilograms, with a destructive power of around 2,000 tons of TNT. Moreover, it appeared that plutonium
Plutonium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, and forms a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibi ...
might be even more fissile
In nuclear engineering, fissile material is material capable of sustaining a nuclear fission chain reaction. By definition, fissile material can sustain a chain reaction with neutrons of thermal energy. The predominant neutron energy may be typ ...
. After conferring with Brigadier General Lucius D. Clay
General Lucius Dubignon Clay (April 23, 1898 – April 16, 1978) was a senior officer of the United States Army who was known for his administration of occupied Germany after World War II. He served as the deputy to General of the Army Dwight D ...
about the construction requirements, Bush drew up a submission for $85 million in fiscal year
A fiscal year (or financial year, or sometimes budget year) is used in government accounting, which varies between countries, and for budget purposes. It is also used for financial reporting by businesses and other organizations. Laws in many ...
1943 for four pilot plants, which he forwarded to Roosevelt on June 17, 1942. With the Army on board, Bush moved to streamline oversight of the project by the OSRD, replacing the Section S-1 with a new S-1 Executive Committee.
Bush soon became dissatisfied with the dilatory way the project was run, with its indecisiveness over the selection of sites for the pilot plants. He was particularly disturbed at the allocation of an AA-3 priority, which would delay completion of the pilot plants by three months. Bush complained about these problems to Bundy and Under Secretary of War Robert P. Patterson
Robert Porter Patterson Sr. (February 12, 1891 – January 22, 1952) was an American judge who served as United States Under Secretary of War, Under Secretary of War under President Franklin D. Roosevelt and US Secretary of War, U.S. Secretary of ...
. Major General Brehon B. Somervell, the commander of the army's Services of Supply
The Services of Supply or "SOS" branch of the Army of the USA was created on 28 February 1942 by Executive Order Number 9082 "Reorganizing the Army and the War Department" and War Department Circular No. 59, dated 2 March 1942. Services of Supp ...
, appointed Brigadier General Leslie R. Groves as project director in September. Within days of taking over, Groves approved the proposed site at Oak Ridge, Tennessee
Oak Ridge is a city in Anderson and Roane counties in the eastern part of the U.S. state of Tennessee, about west of downtown Knoxville. Oak Ridge's population was 31,402 at the 2020 census. It is part of the Knoxville Metropolitan Area. Oak ...
, and obtained a AAA priority. At a meeting in Stimson's office on September 23 attended by Bundy, Bush, Conant, Groves, Marshall Somervell and Stimson, Bush put forward his proposal for steering the project by a small committee answerable to the Top Policy Group. The meeting agreed with Bush, and created a Military Policy Committee chaired by him, with Somervell's chief of staff, Brigadier General Wilhelm D. Styer, representing the army, and Rear Admiral William R. Purnell
Rear Admiral William Reynolds Purnell (6 September 1886 – 3 March 1955) was an officer in the United States Navy who served in World War I and World War II. A 1908 graduate of the United States Naval Academy, he captained destroyers during Wo ...
representing the navy.
At the meeting with Roosevelt on October 9, 1941, Bush advocated cooperating with the United Kingdom, and he began corresponding with his British counterpart, Sir John Anderson John Anderson may refer to:
Business
*John Anderson (Scottish businessman) (1747–1820), Scottish merchant and founder of Fermoy, Ireland
* John Byers Anderson (1817–1897), American educator, military officer and railroad executive, mentor of ...
. But by October 1942, Conant and Bush agreed that a joint project would pose security risks and be more complicated to manage. Roosevelt approved a Military Policy Committee recommendation stating that information given to the British should be limited to technologies that they were actively working on and should not extend to post-war developments. In July 1943, on a visit to London to learn about British progress on antisubmarine technology, Bush, Stimson, and Bundy met with Anderson, Lord Cherwell
Frederick Alexander Lindemann, 1st Viscount Cherwell, ( ; 5 April 18863 July 1957) was a British physicist who was prime scientific adviser to Winston Churchill in World War II.
Lindemann was a brilliant intellectual, who cut through bureauc ...
, and Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 Winston Churchill in the Second World War, dur ...
at 10 Downing Street
10 Downing Street in London, also known colloquially in the United Kingdom as Number 10, is the official residence and executive office of the first lord of the treasury, usually, by convention, the prime minister of the United Kingdom. Along wi ...
. At the meeting, Churchill forcefully pressed for a renewal of interchange, while Bush defended current policy. Only when he returned to Washington did he discover that Roosevelt had agreed with the British. The Quebec Agreement
The Quebec Agreement was a secret agreement between the United Kingdom and the United States outlining the terms for the coordinated development of the science and engineering related to nuclear energy and specifically nuclear weapons. It was s ...
merged the two atomic bomb projects, creating the Combined Policy Committee
The Quebec Agreement was a secret agreement between the United Kingdom and the United States outlining the terms for the coordinated development of the science and engineering related to nuclear energy and specifically nuclear weapons. It was ...
with Stimson, Bush and Conant as United States representatives.
Bush appeared on the cover of ''Time'' magazine on April 3, 1944. He toured the Western Front in October 1944, and spoke to ordnance officers, but no senior commander would meet with him. He was able to meet with Samuel Goudsmit
Samuel Abraham Goudsmit (July 11, 1902 – December 4, 1978) was a Dutch-American physicist famous for jointly proposing the concept of electron spin with George Eugene Uhlenbeck in 1925.
Life and career
Goudsmit was born in The Hague, Neth ...
and other members of the Alsos Mission
The Alsos Mission was an organized effort by a team of British and United States military, scientific, and intelligence personnel to discover enemy scientific developments during World War II. Its chief focus was on the German nuclear energy pro ...
, who assured him that there was no danger from the German project; he conveyed this assessment to Lieutenant General Bedell Smith. In May 1945, Bush became part of the Interim Committee formed to advise the new president, Harry S. Truman
Harry S. Truman (May 8, 1884December 26, 1972) was the 33rd president of the United States, serving from 1945 to 1953. A leader of the Democratic Party, he previously served as the 34th vice president from January to April 1945 under Franklin ...
, on nuclear weapons. It advised that the atomic bomb should be used against an industrial target in Japan as soon as possible and without warning. Bush was present at the Alamogordo Bombing and Gunnery Range
Alamogordo () is the seat of Otero County, New Mexico, United States. A city in the Tularosa Basin of the Chihuahuan Desert, it is bordered on the east by the Sacramento Mountains and to the west by Holloman Air Force Base. The population was ...
on July 16, 1945, for the Trinity nuclear test
Trinity was the code name of the first detonation of a nuclear weapon. It was conducted by the United States Army at 5:29 a.m. on July 16, 1945, as part of the Manhattan Project. The test was conducted in the Jornada del Muerto desert abo ...
, the first detonation of an atomic bomb. Afterwards, he took his hat off to Oppenheimer in tribute.
Before the end of the Second World War, Bush and Conant had foreseen and sought to avoid a possible nuclear arms race
The nuclear arms race was an arms race competition for supremacy in nuclear warfare between the United States, the Soviet Union, and their respective allies during the Cold War. During this same period, in addition to the American and Soviet nuc ...
. Bush proposed international scientific openness and information sharing as a method of self-regulation for the scientific community, to prevent any one political group gaining a scientific advantage. Before nuclear research became public knowledge, Bush used the development of biological weapons as a model for the discussion of similar issues, an "opening wedge". He was less successful in promoting his ideas in peacetime with President Harry Truman, than he had been under wartime conditions with Roosevelt.
In "As We May Think
"As We May Think" is a 1945 essay by Vannevar Bush which has been described as visionary and influential, anticipating many aspects of information society. It was first published in ''The Atlantic'' in July 1945 and republished in an abridged v ...
", an essay published by the ''Atlantic Monthly
''The Atlantic'' is an American magazine and multi-platform publisher. It features articles in the fields of politics, foreign affairs, business and the economy, culture and the arts, technology, and science.
It was founded in 1857 in Boston, ...
'' in July 1945, Bush wrote: "This has not been a scientist's war; it has been a war in which all have had a part. The scientists, burying their old professional competition in the demand of a common cause, have shared greatly and learned much. It has been exhilarating to work in effective partnership."
Post-war years
Memex concept
Bush introduced the concept of thememex
Memex is a hypothetical electromechanical device for interacting with microform documents and described in Vannevar Bush's 1945 article "As We May Think". Bush envisioned the memex as a device in which individuals would compress and store all of ...
during the 1930s, which he imagined as a form of memory augmentation involving a microfilm
Microforms are scaled-down reproductions of documents, typically either photographic film, films or paper, made for the purposes of transmission, storage, reading, and printing. Microform images are commonly reduced to about 4% or of the origin ...
-based "device in which an individual stores all his books, records, and communications, and which is mechanized so that it may be consulted with exceeding speed and flexibility. It is an enlarged intimate supplement to his memory." He wanted the memex to emulate the way the brain links data by association rather than by indexes and traditional, hierarchical storage paradigms, and be easily accessed as "a future device for individual use ... a sort of mechanized private file and library" in the shape of a desk. The memex was also intended as a tool to study the brain itself.
 After thinking about the potential of augmented memory for several years, Bush set out his thoughts at length in "
After thinking about the potential of augmented memory for several years, Bush set out his thoughts at length in "As We May Think
"As We May Think" is a 1945 essay by Vannevar Bush which has been described as visionary and influential, anticipating many aspects of information society. It was first published in ''The Atlantic'' in July 1945 and republished in an abridged v ...
", predicting that "wholly new forms of encyclopedias will appear, ready made with a mesh of associative trails running through them, ready to be dropped into the memex and there amplified". "As We May Think" was published in the July 1945 issue of ''The Atlantic
''The Atlantic'' is an American magazine and multi-platform publisher. It features articles in the fields of politics, foreign affairs, business and the economy, culture and the arts, technology, and science.
It was founded in 1857 in Boston, ...
''. A few months later, ''Life'' magazine published a condensed version of "As We May Think", accompanied by several illustrations showing the possible appearance of a memex machine and its companion devices.
Shortly after "As We May Think" was originally published, Douglas Engelbart
Douglas Carl Engelbart (January 30, 1925 – July 2, 2013) was an American engineer and inventor, and an early computer and Internet pioneer. He is best known for his work on founding the field of human–computer interaction, particularly ...
read it, and with Bush's visions in mind, commenced work that would later lead to the invention of the mouse
A mouse ( : mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus' ...
. Ted Nelson
Theodor Holm Nelson (born June 17, 1937) is an American pioneer of information technology, philosopher, and sociologist. He coined the terms ''hypertext'' and ''hypermedia'' in 1963 and published them in 1965. Nelson coined the terms ''transcl ...
, who coined the terms "hypertext
Hypertext is E-text, text displayed on a computer display or other electronic devices with references (hyperlinks) to other text that the reader can immediately access. Hypertext documents are interconnected by hyperlinks, which are typi ...
" and "hypermedia
Hypermedia, an extension of the term hypertext, is a nonlinear medium of information that includes graphics, audio, video, plain text and hyperlinks. This designation contrasts with the broader term ''multimedia'', which may include non-interac ...
", was also greatly influenced by Bush's essay.
"As We May Think" has turned out to be a visionary and influential essay. In their introduction to a paper discussing information literacy as a discipline, Bill Johnston and Sheila Webber wrote in 2005 that:
Bush was concerned that information overload might inhibit the research efforts of scientists. Looking to the future, he predicted a time when "there is a growing mountain of research. But there is increased evidence that we are being bogged down today as specialization extends. The investigator is staggered by the findings and conclusions of thousands of other workers."
National Science Foundation
The OSRD continued to function actively until some time after the end of hostilities, but by 1946–1947 it had been reduced to a minimal staff charged with finishing work remaining from the war period; Bush was calling for its closure even before the war had ended. During the war, the OSRD had issued contracts as it had seen fit, with just eight organizations accounting for half of its spending. MIT was the largest to receive funds, with its obvious ties to Bush and his close associates. Efforts to obtain legislation exempting the OSRD from the usual governmentconflict of interest
A conflict of interest (COI) is a situation in which a person or organization is involved in multiple interests, financial or otherwise, and serving one interest could involve working against another. Typically, this relates to situations i ...
regulations failed, leaving Bush and other OSRD principals open to prosecution. Bush therefore pressed for OSRD to be wound up as soon as possible.
With its dissolution, Bush and others had hoped that an equivalent peacetime government research and development agency would replace the OSRD. Bush felt that basic research was important to national survival for both military and commercial reasons, requiring continued government support for science and technology; technical superiority could be a deterrent to future enemy aggression. In ''Science, The Endless Frontier'', a July 1945 report to the president, Bush maintained that basic research was "the pacemaker of technological progress". "New products and new processes do not appear full-grown," Bush wrote in the report. "They are founded on new principles and new conceptions, which in turn are painstakingly developed by research in the purest realms of science!" In Bush's view, the "purest realms" were the physical and medical sciences; he did not propose funding the social science
Social science is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among individuals within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the field of sociology, the original "science of soc ...
s. In ''Science, The Endless Frontier'', science historian Daniel Kevles
Daniel J. Kevles (born 2 March 1939 in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania) is an American historian of science best known for his books on American physics and eugenics and for a wide-ranging body of scholarship on science and technology in modern societi ...
later wrote, Bush "insisted upon the principle of Federal patronage for the advancement of knowledge in the United States, a departure that came to govern Federal science policy after World War II."
 In July 1945, the Kilgore bill was introduced in Congress, proposing the appointment and removal of a single science administrator by the president, with emphasis on applied research, and a patent clause favoring a government monopoly. In contrast, the competing Magnuson bill was similar to Bush's proposal to vest control in a panel of top scientists and civilian administrators with the executive director appointed by them. The Magnuson bill emphasized basic research and protected private patent rights. A compromise Kilgore–Magnuson bill of February 1946 passed the Senate but expired in the House because Bush favored a competing bill that was a virtual duplicate of Magnuson's original bill. A Senate bill was introduced in February 1947 to create the National Science Foundation (NSF) to replace the OSRD. This bill favored most of the features advocated by Bush, including the controversial administration by an autonomous scientific board. The bill passed the Senate and the House, but was pocket vetoed by Truman on August 6, on the grounds that the administrative officers were not properly responsible to either the president or Congress. The OSRD was abolished without a successor organization on December 31, 1947.
Without a
In July 1945, the Kilgore bill was introduced in Congress, proposing the appointment and removal of a single science administrator by the president, with emphasis on applied research, and a patent clause favoring a government monopoly. In contrast, the competing Magnuson bill was similar to Bush's proposal to vest control in a panel of top scientists and civilian administrators with the executive director appointed by them. The Magnuson bill emphasized basic research and protected private patent rights. A compromise Kilgore–Magnuson bill of February 1946 passed the Senate but expired in the House because Bush favored a competing bill that was a virtual duplicate of Magnuson's original bill. A Senate bill was introduced in February 1947 to create the National Science Foundation (NSF) to replace the OSRD. This bill favored most of the features advocated by Bush, including the controversial administration by an autonomous scientific board. The bill passed the Senate and the House, but was pocket vetoed by Truman on August 6, on the grounds that the administrative officers were not properly responsible to either the president or Congress. The OSRD was abolished without a successor organization on December 31, 1947.
Without a National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent agency of the United States government that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National I ...
, the military stepped in, with the Office of Naval Research
The Office of Naval Research (ONR) is an organization within the United States Department of the Navy responsible for the science and technology programs of the U.S. Navy and Marine Corps. Established by Congress in 1946, its mission is to plan ...
(ONR) filling the gap. The war had accustomed many scientists to working without the budgetary constraints imposed by pre-war universities. Bush helped create the Joint Research and Development Board (JRDB) of the Army and Navy, of which he was chairman. With passage of the National Security Act on July 26, 1947, the JRDB became the Research and Development Board (RDB). Its role was to promote research through the military until a bill creating the National Science Foundation finally became law. By 1953, the Department of Defense Department of Defence or Department of Defense may refer to:
Current departments of defence
* Department of Defence (Australia)
* Department of National Defence (Canada)
* Department of Defence (Ireland)
* Department of National Defense (Philipp ...
was spending $1.6 billion a year on research; physicists were spending 70 percent of their time on defense related research, and 98 percent of the money spent on physics came from either the Department of Defense or the Atomic Energy Commission (AEC), which took over from the Manhattan Project on January 1, 1947. Legislation to create the National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent agency of the United States government that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National I ...
finally passed through Congress and was signed into law by Truman in 1950.
The authority that Bush had as chairman of the RDB was much different from the power and influence he enjoyed as director of OSRD and would have enjoyed in the agency he had hoped would be independent of the Executive branch and Congress. He was never happy with the position and resigned as chairman of the RDB after a year, but remained on the oversight committee. He continued to be skeptical about rockets and missiles, writing in his 1949 book, ''Modern Arms and Free Men'', that intercontinental ballistic missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological weapons c ...
s would not be technically feasible "for a long time to come ... if ever".
Panels and boards
 With Truman as president, men like John R. Steelman, who was appointed chairman of the President's Scientific Research Board in October 1946, came to prominence. Bush's authority, both among scientists and politicians, suffered a rapid decline, though he remained a revered figure. In September 1949, he was appointed to head a scientific panel that included Oppenheimer to review the evidence that the Soviet Union had tested its first atomic bomb. The panel concluded that it had, and this finding was relayed to Truman, who made the public announcement. During 1952 Bush was one of five members of the
With Truman as president, men like John R. Steelman, who was appointed chairman of the President's Scientific Research Board in October 1946, came to prominence. Bush's authority, both among scientists and politicians, suffered a rapid decline, though he remained a revered figure. In September 1949, he was appointed to head a scientific panel that included Oppenheimer to review the evidence that the Soviet Union had tested its first atomic bomb. The panel concluded that it had, and this finding was relayed to Truman, who made the public announcement. During 1952 Bush was one of five members of the State Department Panel of Consultants on Disarmament The State Department Panel of Consultants on Disarmament, sometimes referred to as the Oppenheimer Panel, was a group created by the United States Department of State that existed from April 1952 to January 1953, during the last year of the Truman a ...
, and led the panel in urging that the United States postpone its planned first test of the hydrogen bomb
A thermonuclear weapon, fusion weapon or hydrogen bomb (H bomb) is a second-generation nuclear weapon design. Its greater sophistication affords it vastly greater destructive power than first-generation nuclear bombs, a more compact size, a lowe ...
and seek a test ban with the Soviet Union, on the grounds that avoiding a test might forestall development of a catastrophic new weapon and open the way for new arms agreements between the two nations. The panel lacked political allies in Washington, however, and the Ivy Mike
Ivy Mike was the codename given to the first full-scale test of a thermonuclear device, in which part of the explosive yield comes from nuclear fusion.
Ivy Mike was detonated on November 1, 1952, by the United States on the island of Elugelab in ...
shot went ahead as scheduled. Bush was outraged when a security hearing stripped Oppenheimer of his security clearance in 1954; he issued a strident attack on Oppenheimer's accusers in ''The New York Times''. Alfred Friendly
Alfred Friendly (December 30, 1911 – November 7, 1983) was an American journalist, editor and writer for ''The Washington Post''. He began his career as a reporter with the ''Post'' in 1939 and became Managing Editor in 1955. In 1967 he cover ...
summed up the feeling of many scientists in declaring that Bush had become "the Grand Old Man of American science".
Bush continued to serve on the NACA through 1948 and expressed annoyance with aircraft companies for delaying development of a turbojet
The turbojet is an airbreathing jet engine which is typically used in aircraft. It consists of a gas turbine with a propelling nozzle. The gas turbine has an air inlet which includes inlet guide vanes, a compressor, a combustion chamber, and ...
engine because of the huge expense of research and development as well as retooling from older piston engines. He was similarly disappointed with the automobile industry, which showed no interest in his proposals for more fuel-efficient engines. General Motors
The General Motors Company (GM) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Automotive industry, automotive manufacturing company headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, United States. It is the largest automaker in the United States and ...
told him that "even if it were a better engine, eneral Motorswould not be interested in it." Bush likewise deplored trends in advertising. "Madison Avenue believes", he said, "that if you tell the public something absurd, but do it enough times, the public will ultimately register it in its stock of accepted verities."
From 1947 to 1962, Bush was on the board of directors for American Telephone and Telegraph
AT&T Corporation, originally the American Telephone and Telegraph Company, is the subsidiary of AT&T Inc. that provides voice, video, data, and Internet telecommunications and professional services to businesses, consumers, and government agen ...
. He retired as president of the Carnegie Institution and returned to Massachusetts in 1955, but remained a director of Metals and Controls Corporation from 1952 to 1959, and of Merck & Co. 1949–1962. Bush became chairman of the board at Merck following the death of George W. Merck
George Wilhelm Herman Emanuel Merck (March 29, 1894 – November 9, 1957) was the president of Merck & Co. from 1925 to 1950 and a member of the Merck family.
Early life
George W. Merck was born in New York City, to George Friedrich and Fri ...
, serving until 1962. He worked closely with the company's president, Max Tishler
Max Tishler (October 30, 1906 – March 18, 1989) was president of Merck Sharp and Dohme Research Laboratories where he led the research teams that synthesized ascorbic acid, riboflavin, cortisone, pyridoxine, pantothenic acid, nicotinamide, ...
, although Bush was concerned about Tishler's reluctance to delegate responsibility. Bush distrusted the company's sales organization, but supported Tishler's research and development efforts. He was a trustee of Tufts College 1943–1962, of Johns Hopkins University 1943–1955, of the Carnegie Corporation of New York 1939–1950, the Carnegie Institution of Washington 1958–1974, and the George Putnam Fund of Boston 1956–1972, and was a regent of the Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums and education and research centers, the largest such complex in the world, created by the U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Founded ...
1943–1955.
Final years and death
After suffering a stroke, Bush died inBelmont, Massachusetts
Belmont is a town in Middlesex County, Massachusetts. It is a western suburb of Boston, Massachusetts, United States; and is part of the Greater Boston metropolitan area. At the time of the 2020 U.S. Census, the town's population stood at 27,295 ...
, at the age of 84 from pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severity ...
on June 28, 1974. He was survived by his sons Richard (a surgeon) and John (president of Millipore Corporation
Merck Millipore was the brand used by Merck KGaA, Merck Group's (not US-based Merck & Co.) global life science business until 2015 when the company re-branded. It was formed when Merck acquired the Millipore Corporation in 2010. Merck is a suppl ...
) and by six grandchildren and his sister Edith. Bush's wife had died in 1969. He was buried at South Dennis Cemetery in South Dennis, Massachusetts
South Dennis is a census-designated place (CDP) in the town of Dennis in Barnstable County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 3,643 at the 2010 census, the most of the 5 CDPs in Dennis.
Geography
South Dennis is located on Cape Co ...
, after a private funeral service. At a public memorial subsequently held by MIT, Jerome Wiesner
Jerome Bert Wiesner (May 30, 1915 – October 21, 1994) was a professor of electrical engineering, chosen by President John F. Kennedy as chairman of his Science Advisory Committee (PSAC). Educated at the University of Michigan, Wiesner was assoc ...
declared "No American has had greater influence in the growth of science and technology than Vannevar Bush".
Awards and honors
*Bush received theAIEE
The American Institute of Electrical Engineers (AIEE) was a United States-based organization of electrical engineers that existed from 1884 through 1962. On January 1, 1963, it merged with the Institute of Radio Engineers (IRE) to form the Institu ...
's Edison Medal
The IEEE Edison Medal is presented by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) "for a career of meritorious achievement in electrical science, electrical engineering, or the electrical arts." It is the oldest medal in this fi ...
in 1943, "for his contribution to the advancement of electrical engineering, particularly through the development of new applications of mathematics to engineering problems, and for his eminent service to the nation in guiding the war research program."
*In 1945, Bush was awarded the Public Welfare Medal The Public Welfare Medal is awarded by the U.S. National Academy of Sciences "in recognition of distinguished contributions in the application of science to the public welfare." It is the most prestigious honor conferred by the academy. First awar ...
from the National Academy of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the Nati ...
.
*In 1949, he received the IRI Medal The IRI Medal, established by the Industrial Research Institute (IRI) in 1946, recognizes and honors leaders of technology for their outstanding accomplishments in technological innovation which contribute broadly to the development of industry and ...
from the Industrial Research Institute
Innovation Research Interchange (IRI) is a division of the National Association of Manufacturers, a nonprofit association based in Washington, D. C., United States. IRI was founded as a private non-profit in 1938 and merged with the NAM in 2022. IR ...
in recognition of his contributions as a leader of research and development.
*President Truman awarded Bush the Medal of Merit with bronze oak leaf cluster in 1948.
*President Lyndon Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), often referred to by his initials LBJ, was an American politician who served as the 36th president of the United States from 1963 to 1969. He had previously served as the 37th vice ...
awarded him the National Medal of Science
The National Medal of Science is an honor bestowed by the President of the United States to individuals in science and engineering who have made important contributions to the advancement of knowledge in the fields of behavioral and social scienc ...
in 1963.
*President Richard Nixon
Richard Milhous Nixon (January 9, 1913April 22, 1994) was the 37th president of the United States, serving from 1969 to 1974. A member of the Republican Party, he previously served as a representative and senator from California and was ...
presented him, as well as James B. Conant
James Bryant Conant (March 26, 1893 – February 11, 1978) was an American chemist, a transformative President of Harvard University, and the first U.S. Ambassador to West Germany. Conant obtained a Ph.D. in Chemistry from Harvard in 1916. ...
and General Leslie R. Groves with the unique Atomic Pioneers Award from the Atomic Energy Commission in February 1970.
*Bush was made a Knight Commander of the Order of the British Empire
The Most Excellent Order of the British Empire is a British order of chivalry, rewarding contributions to the arts and sciences, work with charitable and welfare organisations,
and public service outside the civil service. It was established ...
in 1948, and an Officer of the French Legion of Honor
The National Order of the Legion of Honour (french: Ordre national de la Légion d'honneur), formerly the Royal Order of the Legion of Honour ('), is the highest French order of merit, both military and civil. Established in 1802 by Napoleon ...
in 1955.
In 1980, the National Science Foundation created the Vannevar Bush Award
The National Science Board established the Vannevar Bush Award ( ) in 1980 to honor Vannevar Bush's unique contributions to public service. The annual award recognizes an individual who, through public service activities in science and technology ...
to honor his contributions to public service. The Vannevar Bush papers are located in several places, with the majority of the collection held at the Library of Congress. Additional papers are held by the MIT Institute Archives and Special Collections, the Carnegie Institution, and the National Archives and Records Administration.

See also
*List of pioneers in computer science
This is a list of people who made transformative breakthroughs in the creation, development and imagining of what computers could do.
Pioneers
: ''To arrange the list by date or person (ascending or descending), click that column's small "up-do ...
Bibliography
(complete list of published papers: ). * * * * * * *Notes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* *Vannevar Bush Papers
MC-0078. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Department of Distinctive Collections, Cambridge, Massachusetts. * * * * * * , - , - , - {{DEFAULTSORT:Bush, Vannevar 1890 births 1974 deaths 20th-century American engineers 20th-century American inventors American electrical engineers American futurologists American people of English descent Burials in Massachusetts Fellows of the American Physical Society Honorary Knights Commander of the Order of the British Empire IEEE Edison Medal recipients IEEE Lamme Medal recipients Internet pioneers Manhattan Project people Medal for Merit recipients MIT School of Engineering alumni MIT School of Engineering faculty National Medal of Science laureates Office of Science and Technology Policy officials People from Chelsea, Massachusetts People from Everett, Massachusetts Raytheon Company people Recipients of the Legion of Honour Tufts University School of Engineering alumni